|
 |
Iran Update, January 27, 2024

Iran Update, January 27, 2024
Andie Parry, Annika Ganzeveld, Johanna Moore, and Nicholas Carl
Information Cutoff: 2:00 pm EST
The Iran Update provides insights into Iranian and Iranian-sponsored activities abroad that undermine regional stability and threaten US forces and interests. It also covers events and trends that affect the stability and decision-making of the Iranian regime. The Critical Threats Project (CTP) at the American Enterprise Institute and the Institute for the Study of War (ISW) provides these updates regularly based on regional events. For more on developments in Iran and the region, see our interactive map of Iran and the Middle East.
Note: CTP and ISW have refocused the update to cover the Israel-Hamas war. The new sections address developments in the Gaza Strip, the West Bank, Lebanon, and Syria, as well as noteworthy activity from Iran’s Axis of Resistance. We do not report in detail on war crimes because these activities are well-covered in Western media and do not directly affect the military operations we are assessing and forecasting. We utterly condemn violations of the laws of armed conflict and the Geneva Conventions and crimes against humanity even though we do not describe them in these reports.
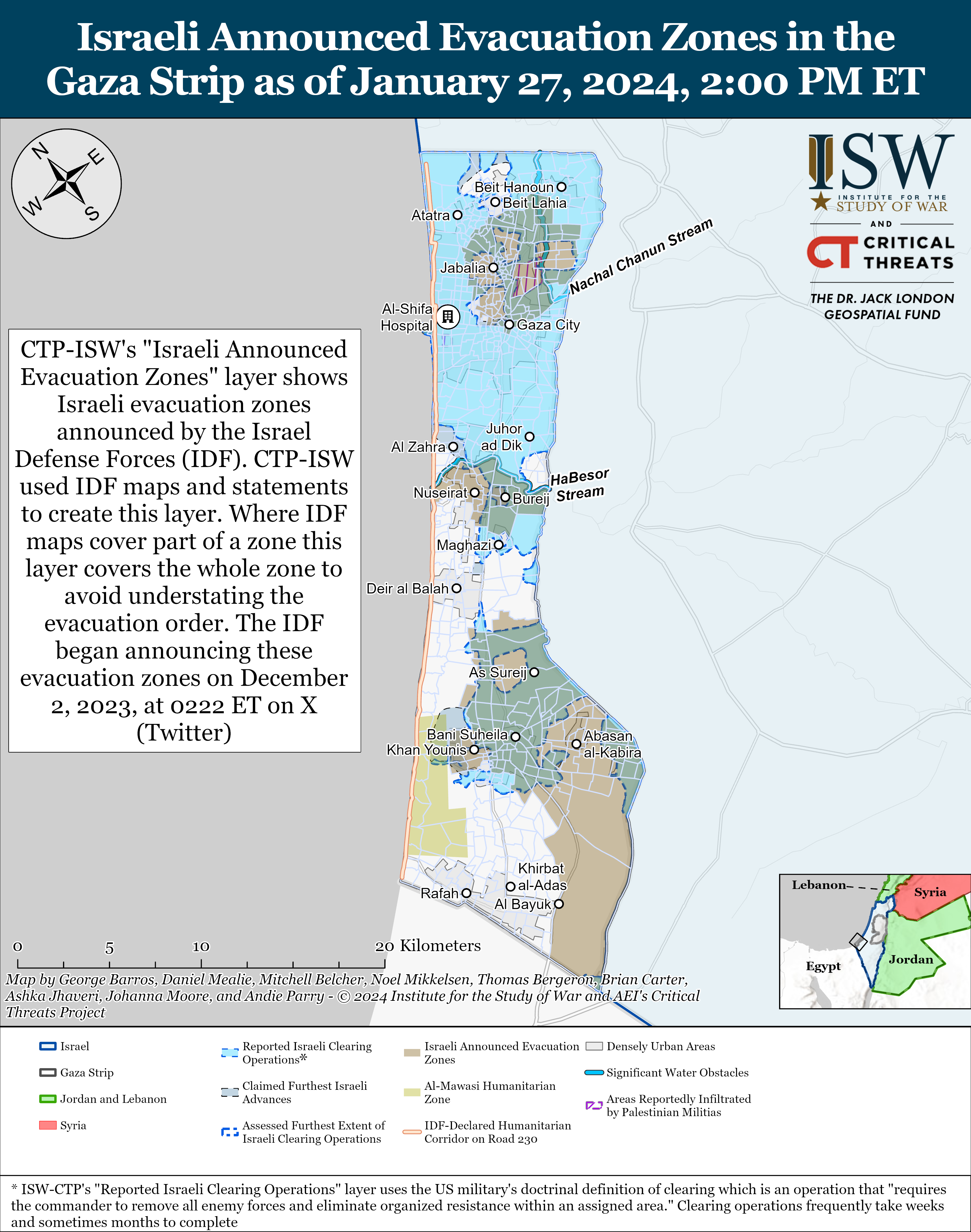
Click here to see CTP and ISW’s interactive map of Israeli ground operations. This map is updated daily alongside the static maps present in this report. Click here to subscribe to the Iran Update.
Key Takeaways:
- Northern Gaza Strip: Palestinian fighters claimed clashes with Israeli forces. Hamas and other Palestinian fighters have contested Israeli raids in certain areas of the northern Gaza Strip throughout January 2024.
- Central Gaza Strip: Palestinian Islamic Jihad’s militant wing targeted an Israeli supply line with mortars and rockets.
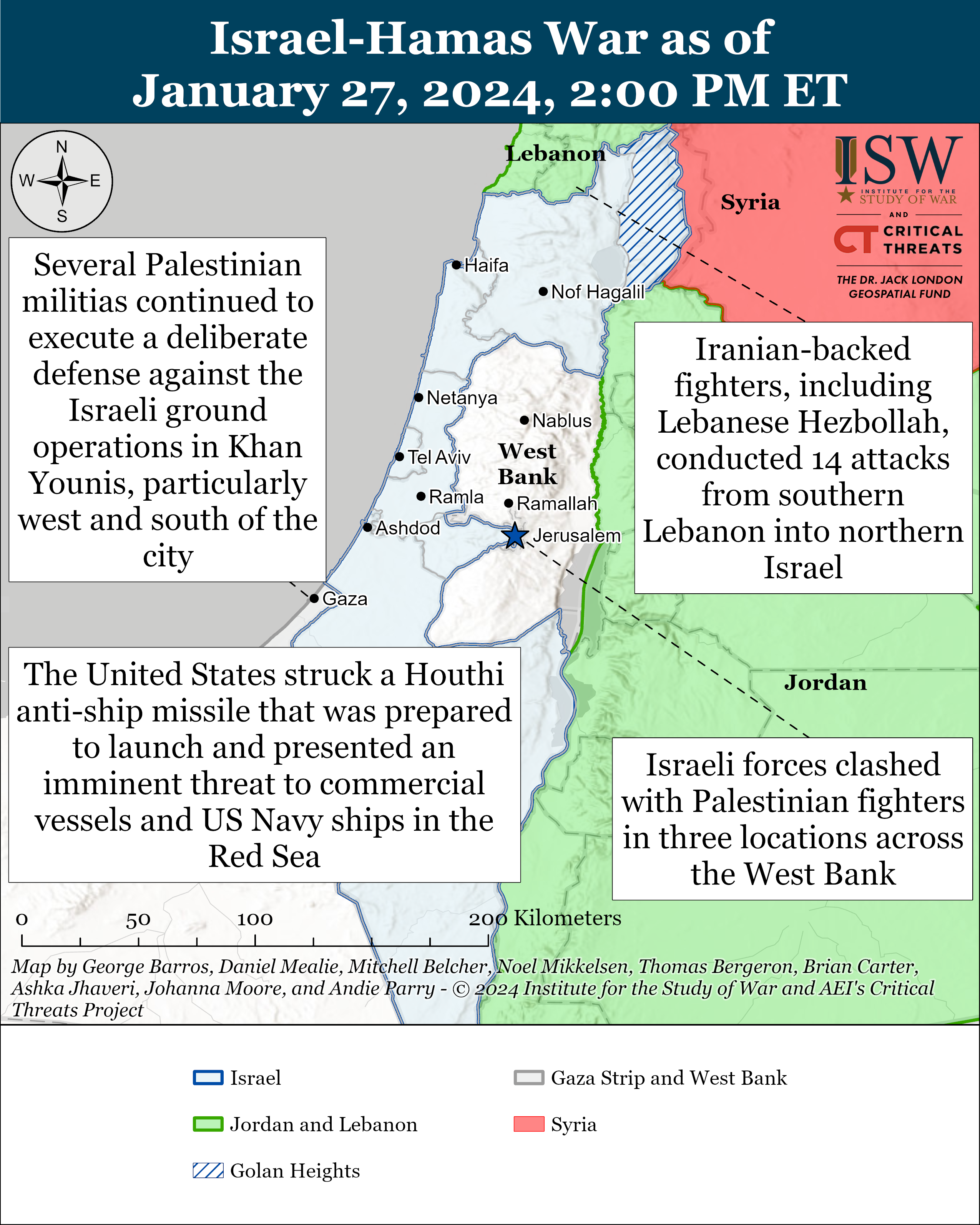
- Southern Gaza Strip: The Israel Defense Forces 98th Division destroyed weapons warehouses and clashed with Palestinian fighters in western Khan Younis. Several Palestinian militias, including Hamas, continued to execute a deliberate defense against the Israeli ground operations in Khan Younis, particularly west and south of the city.
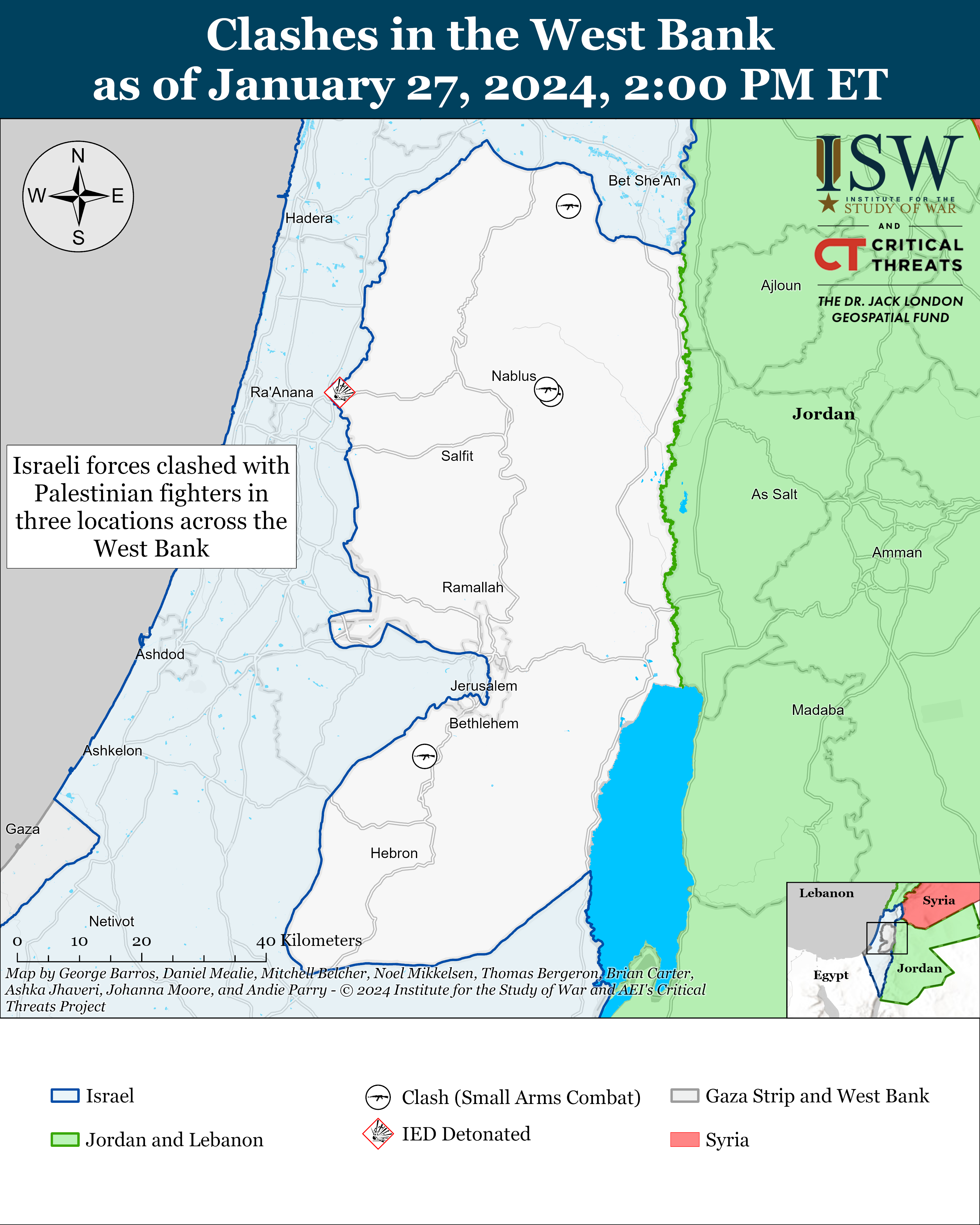
- West Bank: Israeli forces clashed with Palestinian fighters in three locations.
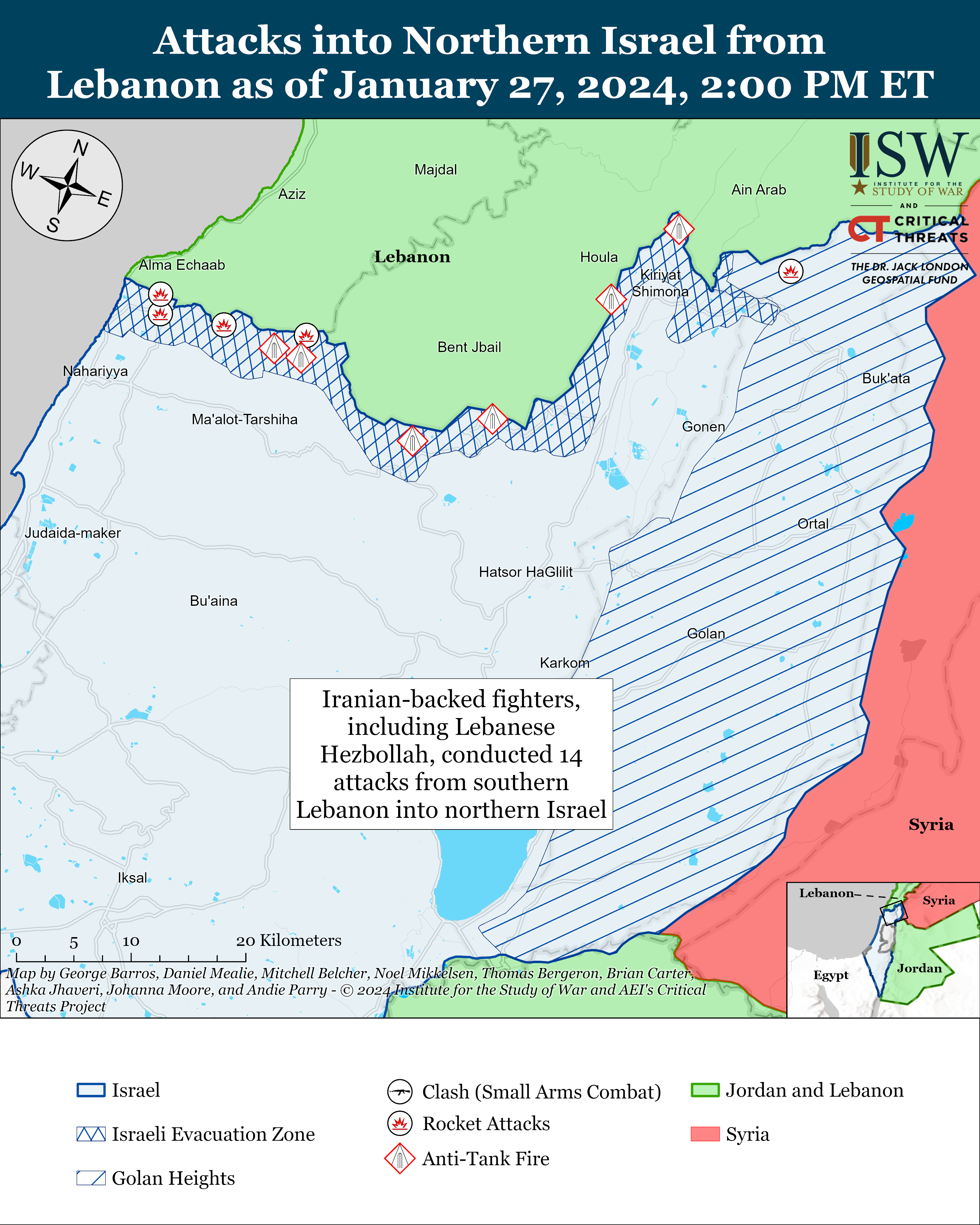
- Southern Lebanon and Golan Heights: Iranian-backed fighters, including Lebanese Hezbollah, conducted 14 attacks from southern Lebanon into northern Israel.
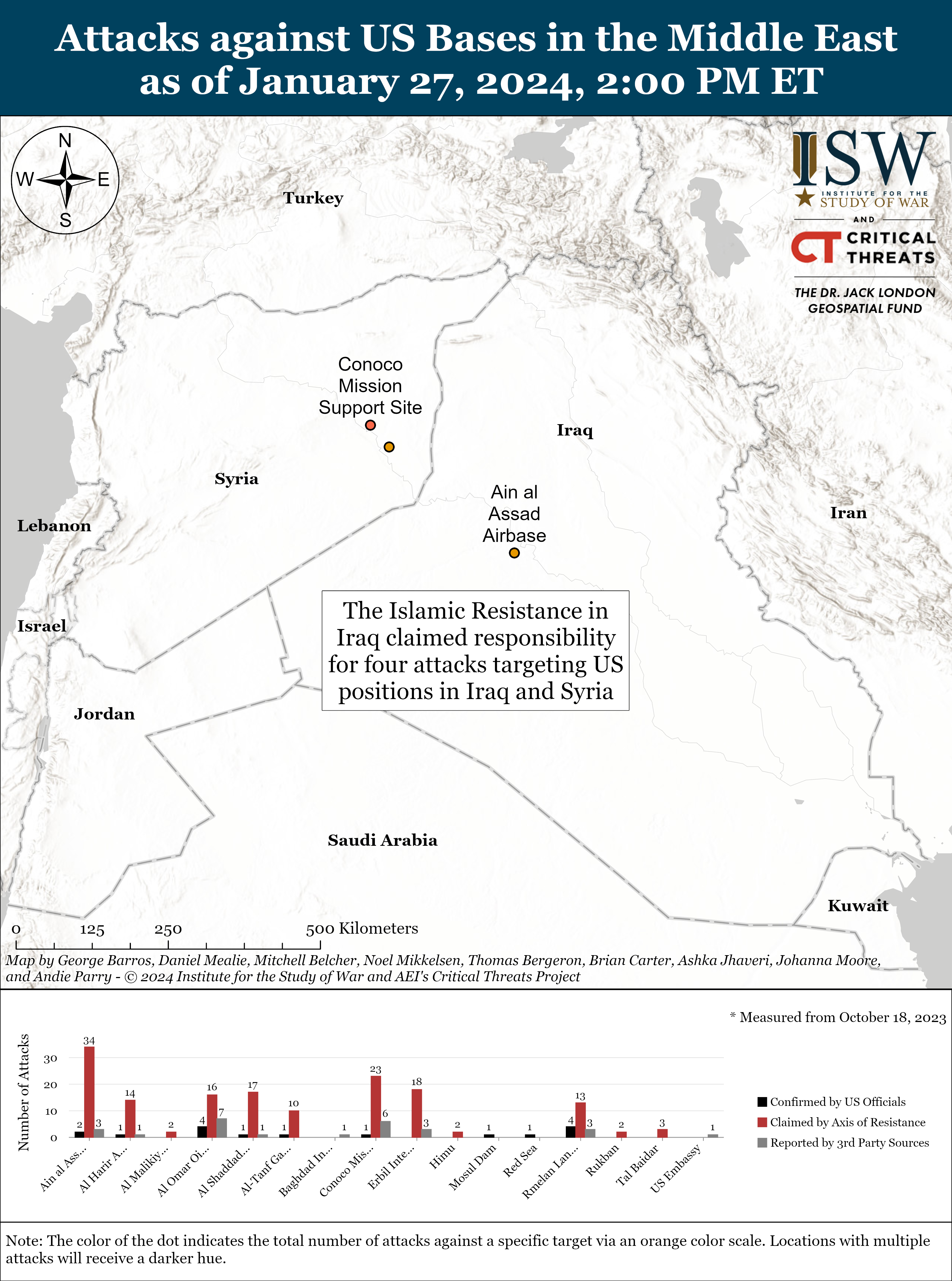
- Iraq and Syria: The Islamic Resistance in Iraq—a coalition of Iranian-backed Iraqi militias—claimed responsibility for four attacks targeting US positions in Iraq and Syria.
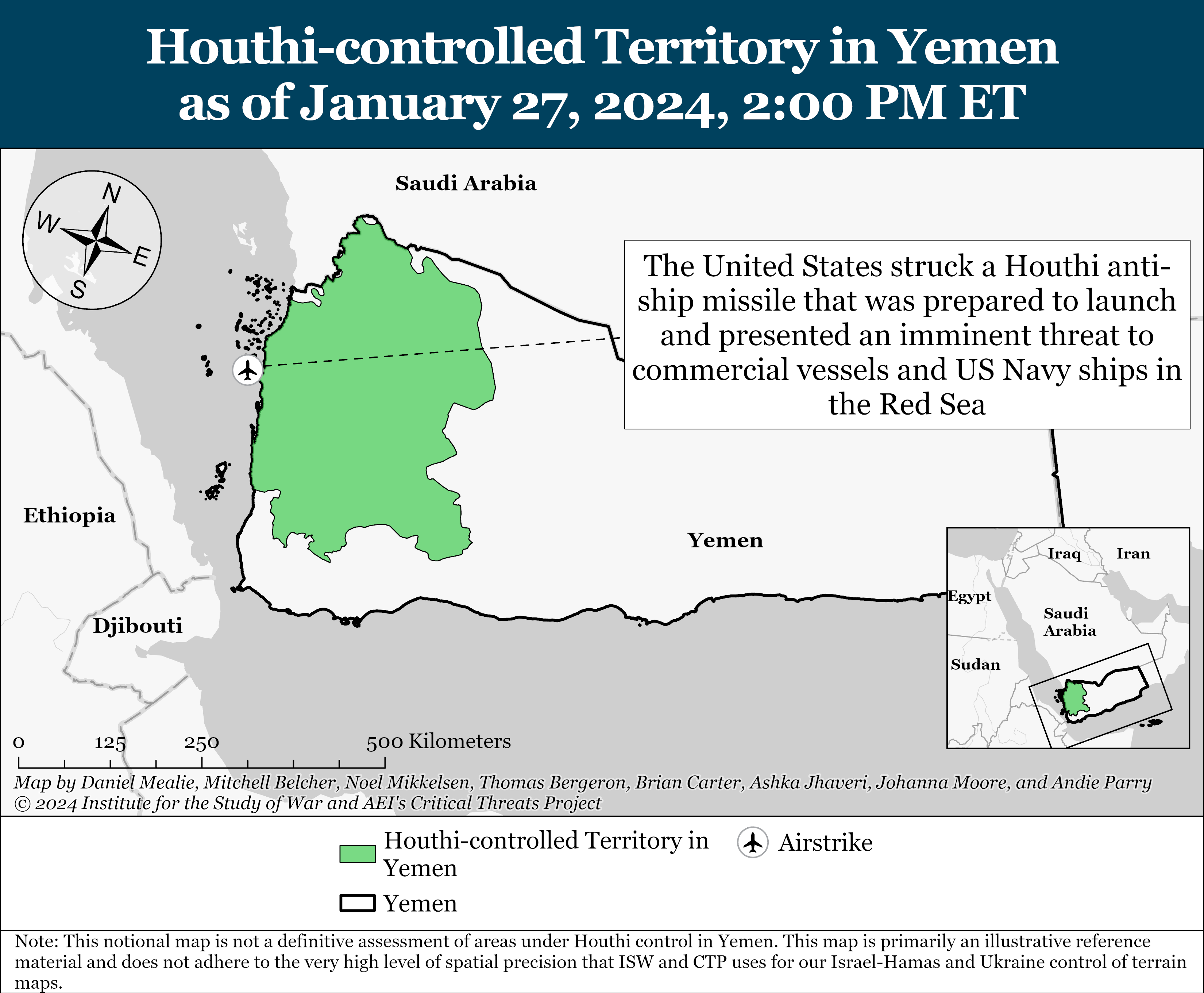
- Yemen: US Central Command announced that the United States struck a Houthi anti-ship missile that was prepared to launch and presented an imminent threat to commercial vessels and US Navy ships in the Red Sea.
Gaza Strip
Axis of Resistance campaign objectives:
- Erode the will of the Israeli political establishment and public to launch and sustain a major ground operation into the Gaza Strip
- Degrade IDF material and morale around the Gaza Strip.
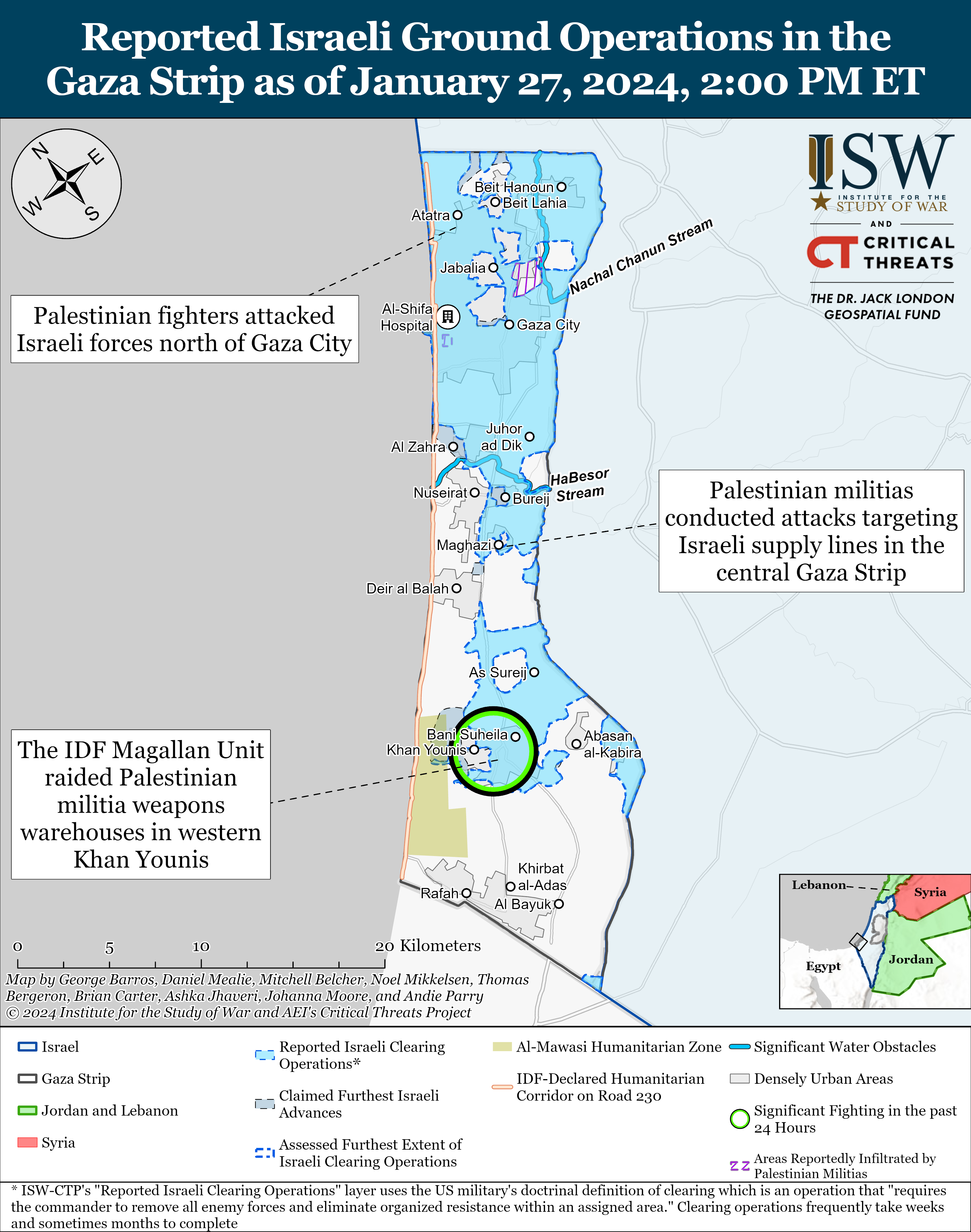
Palestinian fighters claimed clashes with Israeli forces in the northern Gaza Strip. The al Aqsa Martyrs’ Brigades, which is the self-proclaimed military wing of Fatah, targeted Israeli forces in the al Atatra area north of Gaza City.[1] Hamas and other Palestinian fighters have contested Israeli raids in certain areas of the northern Gaza Strip throughout January 2024.
Palestinian Islamic Jihad (PIJ)’s militant wing targeted an IDF supply line into the central Gaza Strip with mortars and rockets on January 27.[2]
The Israel Defense Forces (IDF) 98th Division destroyed weapons warehouses and clashed with Palestinian fighters in western Khan Younis on January 27. The IDF stated its 89th Commando forces have killed over 100 Palestinian fighters operating in western Khan Younis in the past week.[3] The IDF Magallan Unit operating under the 89th Commandos raided Palestinian militia weapons sites as the corresponding fire group conducted airstrikes on three Palestinian fighters burying charges near IDF ground forces.[4] The Egoz Command Unit raided a house that belonged to an associate of Yahya Sinwar and a weapons warehouse in Khan Younis.[5]
Several Palestinian militias, including Hamas, continued to execute a deliberate defense against the Israeli ground operations in Khan Younis, particularly west and south of the city. The militant wings of Hamas, PIJ, the al Aqsa Martyrs Brigades, and the Democratic Front for the Liberation of Palestine (DFLP) claimed several attacks targeting Israeli infantry and armor with small arms, RPGs, and mortars in western Khan Younis.[6] The DFLP is a leftist Palestinian militia aligned with Hamas in the war.
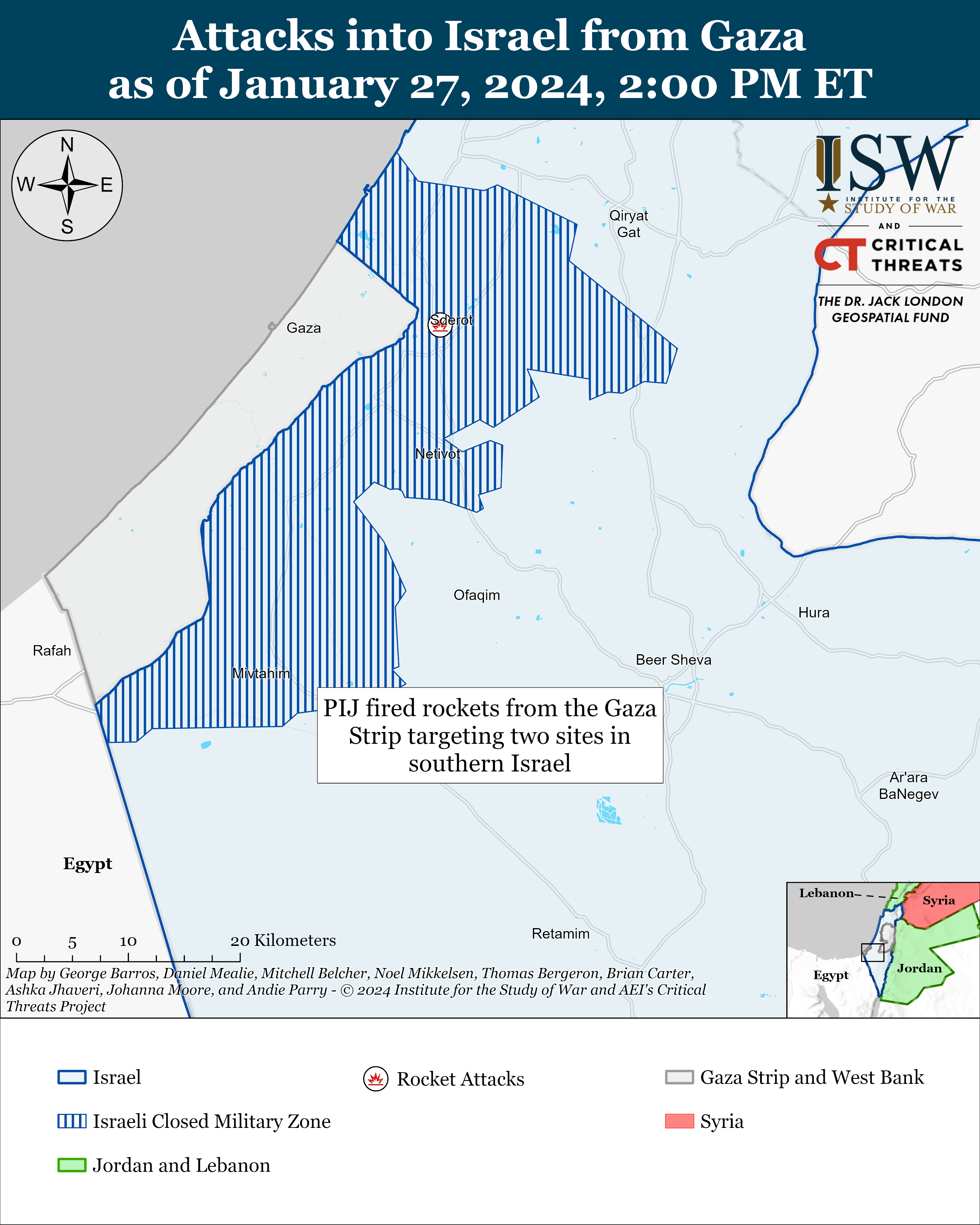
Palestinian militias conducted two indirect fire attacks from the Gaza Strip into southern Israel on January 27. PIJ fired rockets targeting Sderot and Nir Am.[7]
Recorded reports of attacks; CTP-ISW cannot independently verify impact.
West Bank
Axis of Resistance campaign objectives:
- Draw IDF assets and resources toward the West Bank and fix them there
Israeli forces clashed with Palestinian fighters in three locations across the West Bank.[8] The al Aqsa Martyrs’ Brigades targeted Israeli forces three times using small arms fire and IEDs.[9] Its fighters also fired on an Israeli settlement near Hebron.[10]
This map is not an exhaustive depiction of clashes and demonstrations in the West Bank.
Southern Lebanon and Golan Heights
Axis of Resistance campaign objectives:
- Draw IDF assets and resources toward northern Israel and fix them there
- Set conditions for successive campaigns into northern Israel
Iranian-backed fighters, including Lebanese Hezbollah, conducted 14 attacks from southern Lebanon into northern Israel on January 27.[11] This rate of attacks is well over double this week’s average of 5.8 attacks per day. Hezbollah conducted 13 attacks primarily targeting Israeli military forces and infrastructure.[12]
Recorded reports of attacks; CTP-ISW cannot independently verify impact.
Iran and Axis of Resistance
Axis of Resistance campaign objectives:
- Demonstrate the capability and willingness of Iran and the Axis of Resistance to escalate against the United States and Israel on multiple fronts
- Set conditions to fight a regional war on multiple fronts
The Islamic Resistance in Iraq—a coalition of Iranian-backed Iraqi militias—claimed responsibility for four attacks targeting US positions in Iraq and Syria. The Islamic Resistance in Iraq claimed separate drone attacks targeting US forces at al Omar oilfield and Conoco Mission Support Site in Deir ez Zor Province on January 26.[13] The Islamic Resistance in Iraq claimed a rocket attack targeting US forces at Conoco on January 27.[14] The group also claimed a drone attack targeting US forces at Ain al Assad airbase in Anbar Province, Iraq, on January 27.[15]
US Central Command (CENTCOM) announced that the United States struck a Houthi anti-ship missile that was prepared to launch and presented an imminent threat to commercial vessels and US Navy ships in the Red Sea on January 27.[16] Houthi-controlled outlet al Masirah claimed on January 27 that the United States and United Kingdom conducted two airstrikes targeting Ras Issa, which is Yemen’s main oil export terminal.[17] It is unclear whether the CENTCOM announcement and al Masirah claim are referring to the same incident. The US strike follows the Houthis’ anti-ship missile attack targeting the British-owned, Marshall Islands-flagged commercial oil tanker Marlin Luanda on January 26.[18] The attack caused a 19-hour fire at one of the vessel’s tanks, making it the “most damaging” Houthi attack since the Houthis started their attack campaign targeting international shipping in October 2023.[19]

[1] https://t.me/elaqsa_1965/5564
[2] https://t.me/sarayaps/17318 ; https://t.me/sarayaps/17317
[3] https://www dot idf.il/176602
[4] https://twitter.com/idfonline/status/1751136736036421653 ; https://www dot idf.il/176602
[5] https://twitter.com/AvichayAdraee/status/1751201817050890283
[6] https://t.me/sarayaps/17319 ; https://t.me/elaqsa_1965/5563 ; https://t.me/sarayaps/17312 ;
https://t.me/qassam1brigades/1475 ; https://t.me/kataeb_moqawma/4106 ; https://t.me/kataeb_moqawma/4107 ; https://t.me/qassam1brigades/1478
[7] https://t.me/sarayaps/17313
[8] https://t.me/QudsN/363153 ; https://t.me/QudsN/363159 ; https://t.me/QudsN/363189
[9] https://t.me/elaqsa_1965/5561 ; https://t.me/elaqsa_1965/5560 ; https://t.me/QudsN/363189
[10] https://t.me/elaqsa_1965/5567
[11] https://t.me/C_Military1/44761 ; https://t.me/C_Military1/44763 ; https://t.me/C_Military1/44765 ; https://t.me/C_Military1/44766 ; https://t.me/C_Military1/44778 ; https://t.me/C_Military1/44779 ; https://t.me/C_Military1/44795 ; https://t.me/C_Military1/44797 ; https://t.me/C_Military1/44801 ; https://t.me/C_Military1/44803 ; https://t.me/C_Military1/44815 ; https://t.me/C_Military1/44817 ; https://t.me/C_Military1/44819 ; https://t.me/C_Military1/44781
[12] https://t.me/C_Military1/44761 ; https://t.me/C_Military1/44763 ; https://t.me/C_Military1/44765 ; https://t.me/C_Military1/44766 ; https://t.me/C_Military1/44778 ; https://t.me/C_Military1/44779 ; https://t.me/C_Military1/44795 ; https://t.me/C_Military1/44797 ; https://t.me/C_Military1/44801 ; https://t.me/C_Military1/44803 ; https://t.me/C_Military1/44815 ; https://t.me/C_Military1/44817 ; https://t.me/C_Military1/44819
[13] https://t.me/elamharbi/257
[14] https://t.me/elamharbi/258
[15] https://t.me/elamharbi/259
[16] https://twitter.com/CENTCOM/status/1751071115147985236
[17] https://www.reuters.com/world/middle-east/houthis-tv-says-us-british-air...
[18] https://twitter.com/army21ye/status/1750956891411247542
[19] https://www.ft.com/content/74eca55a-2185-44c8-b367-effbcc00d265